JavaScript 数据结构
一、概述
数据结构是指相互之间存在一种或多种特定关系的数据组成的集合。采用合适的数据结构能给提高开发或者存储效率。比如我们学习Js时接触过的数据结构(Set、Map),在合适的时机使用它们能帮助我们更快的解决问题。
本阶段我们会学习自己创建几种数据结构,来帮助我们在日后的开发中解决特定的某类问题。
二、栈
1. 创建栈结构
栈是一种遵循后进先出(LIFO)原则的有序数据集。
栈顶、栈底、入栈、出栈 栈结构也被用在编译器和内存中保存变量等
下面我们来创建栈数据结构。功能需求:
添加数据(push)
返回栈顶数据(peek)
从栈中删除栈顶数据并返回(pop)
清空栈(clear)
返回栈中数据个数(size)
class Stack{
constructor(){
this.items = [];
}
push(...rest){
rest.forEach(v=>{
this.items.push(v);
});
return this.items.length;
}
peek(){
return this.items[this.items.length-1];
}
pop(){
return this.items.pop();
}
clear(){
this.items = [];
}
size(){
return this.items.length;
}
}
检测是否满足栈的规则。
2. 栈结构的应用
- 进制转换 (Js自带进制转换api,此案例并不实用,仅作为理解原理)
//2进制转换
function baseConverter2(number){
let stack = new Stack();
let result = "";
while(number>0){
stack.push(number
number = Math.floor(number/2);
}
while(stack.size()){
result += stack.pop();
}
return result||"0";
}
console.log(baseConverter2(8));
//16进制转换
function baseConverter16(number,base=2) {
let stack = new Stack();
let sign = "0123456789abcdefg";
let result = "";
while (number>0){
let remainder = number
stack.push(sign[remainder]);
number = Math.floor(number/base);
}
while(stack.size()){
result += stack.pop();
}
return result||"0";
}
console.log(baseConverter16(15,16));
- 判断回文字符串
//判断回文
function isPlalindrome(word){
if( !word || typeof word !== "string" ){
throw "参数不为字符或字符为空,我们返回了false";
return false
};
let stack = new Stack();
let back = ""
stack.push(...word);
while (stack.size()){
back += stack.pop();
}
return back === word;
}
console.log(isPlalindrome("我爱你你爱我"));
console.log(isPlalindrome("123456"));
- 检测括号匹配
//检测括号匹配
function ifSignMatch(str){
let leftSign = "{[(",
rightSign = "}])";
let stack = new Stack();
for(let i=0,len=str.length;&ilt;len;i++){
let char = str.charAt(i);
//遇到左括号,入栈
if( leftSign.indexOf(char) !== -1 ){
stack.push(char);
}
//遇到右括号,匹配
else if( rightSign.indexOf(char) !== -1 ){
if( leftSign.indexOf(stack.pop()) !== rightSign.indexOf(char) ){
return false;
}
}
}
return stack.size() === 0;
}
console.log(ifSignMatch("{[()]}"));
console.log(ifSignMatch("{[()]}}"));
3. 思考
this.items这可是一个任意都可以直接访问的数组,直接放着也沙雕了吧…想一下有什么样的方式可以避免外界的访问呢?比如 闭包?Symbol ?
三、队列
1. 创建队列结构
队列是一种遵循先进先出(FIFO)原则的有序数据集。
类似场景举例… 入队、出队
下面我们来创建队列数据结构。功能需求:
入队(enqueue)
出队(dequeue)
返回队列首端数据,但不删除(first)
清空队列(clear)
返回队列长度(size)
//队列结构
class Queue{
constructor(){
this.items = [];
}
enqueue(...rest){
rest.forEach(v=>{
this.items.push(v);
})
}
dequeue(){
return this.items.shift();
}
first(){
return this.items[0];
}
clear(){
this.items = [];
}
size(){
return this.items.length;
}
}
测试…
优化,避免直接访问items
let Queue = (function(){
let symbol = Symbol();
return class{
constructor(){
this[symbol] = [];
}
enqueue(...rest){
rest.forEach(v=>{
this[symbol].push(v);
});
}
dequeue(){
return this[symbol].shift();
}
first(){
return this[symbol][0];
}
clear(){
this[symbol] = [];
}
size(){
return this[symbol].length;
}
}
})();
2. 队列结构的应用
队列是极其基础的一种数据结构,不管在哪都能够运用到,通常都需要配合其他的代码实现强大的功能。比如整个JavaScript的执行机制,因为其实单线程,所以多任务之间都是队列的形式排好然后执行,再借助事件循环实现这个JavaScript强大的功能。比如jQuery中我们学习过的queue队列,最基本的结构就是我们刚刚介绍的队列。所以说我们其实在非常多的地方都在使用着队列,因为它实在太常见太实用了,只不过,使用时的api已经写好的而不需要我们自己来定义实现。
- 基于队列实现类似于jq的动画队列
//动画队列
let aq = (function(){
//可以将Queue提出,这样不仅仅在aq这个功能下能用到
class Queue{
constructor(){
this.items = [];
}
enqueue(...rest){
rest.forEach(v=>{
this.items.push(v);
});
}
dequeue(){
return this.items.shift();
}
first(){
return this.items[0];
}
clear(){
this.items = [];
}
size(){
return this.items.length;
}
}
//继承Queue,实现一个适合于当前需求的类
class _Queue extends Queue{
constructor(){
super();
this.ifDone = true;
}
run(){
if( !this.ifDone ){
return;
};
this.ifDone = false;
!function d(){
if( this.size() ){
new Promise(this.dequeue())
.then(d.bind(this));
}else{
this.ifDone = true;
}
}.call(this)
}
next(){
this.dequeue()();
}
}
//Map数据结构,用于
let animateQueue = new Map();
class Init{
constructor(selector){
this.dom = document.querySelector(selector);
}
animate(options,time=300){
if( !animateQueue.get(this.dom)){
animateQueue.set(this.dom,new _Queue());
}
let queue = animateQueue.get(this.dom);
queue.enqueue(function(res){
this.style.transition = time/1000+"s";
this.offsetWidth;
for (let [key,value] of Object.entries(options)) {
this.style[key] = value+'px';
}
setTimeout(res,time);
}.bind(this.dom));
queue.run();
return this;
}
}
return function(selector){
return new Init(selector)
}
})();
3. 优先队列
根据优先级来决定插入的顺序,就好像登机时的贵宾通道一样…
let PriorityQueue = (function(){
let symbol = Symbol();
class Priority{
constructor(ele,pri){
this.element = ele;
this.priority = pri;
}
}
return class{
constructor(){
this[symbol] = [];
}
enqueue(element,priority){
let pri = new Priority(element,priority);
let i=0;
for (;&ilt;this.size();i++){
if( this[symbol][i].priority > priority ){
break;
}
}
this[symbol].splice(i,0,pri);
}
dequeue(){
return this[symbol].shift().element;
}
first(){
return this[symbol][0].element;
}
clear(){
this[symbol] = [];
}
size(){
return this[symbol].length;
}
}
})();
let priorityQueue = new PriorityQueue();
priorityQueue.enqueue("afei",1)
priorityQueue.enqueue("zhuque",0)
priorityQueue.enqueue("wula",1)
console.log(priorityQueue.dequeue());
console.log(priorityQueue.dequeue());
console.log(priorityQueue.dequeue());
此处我们是通过在入队的时候的排序实现优先级的,同样的,我们能不能从出队的角度来实现呢?或者,还有没有什么其他的方式来做呢?
4. 双向队列
允许从前面添加取出,也允许从后面添加取出。
//双向队列
let Queue = (function(){
let symbol = Symbol();
return class{
constructor(){
this[symbol] = [];
}
enqueueFront(ele){
this[symbol].unshift(ele);
}
enqueueBack(ele){
this[symbol].push(ele);
}
dequeueFront(){
return this[symbol].shift();
}
dequeueBack(){
return this[symbol].pop();
}
front(){
return this[symbol][0];
}
back(){
return this[symbol][this.size()-1];
}
size(){
return this[symbol].length;
}
}
})();
四、链表
1. 创建链表结构
存储多个数据常见的结构就是数组,它提供非常方便的[ ]操作符。但是缺点是,当我们往数组中插入或删除数据时,后面所有元素的位置都要进行一次变化。即使提供了便捷的splice函数,但内部原理上还是一样的。所以,当数据较多,并且会频繁的插入/删除数据时,再用数组来充当存储结构效率是较低的。
链表(Linked List)也可以用来存储有序的数据,它与数组的不同在于,并不是在内存中连续的存储,而是每一个节点由自身的数据和指向下一个节点的next组成,通过next指针将所有的节点串联起来形成类似于链的结构。
下面我们来创建链表结构:
链尾添加节点(append)
查找指定数据对应的节点(find)
指定数据后面插入节点(insert)
移除指定数据对应的节点(remove)
打印链表数据(print)
返回链表长度(size)
//可能额外需要的功能
查找数据对应索引(indexOf)
按照索引查找节点(find的参数设计)
按照索引插入节点(insert的参数设计)
按照索引移除节点(remove的参数数据)
//详细分解请看直播课讲解
let LinkedList = (function(){
let HEAD = Symbol();
class Node{
constructor(data){
this.data = data;
this.next = null;
}
}
return class{
constructor(){
this[HEAD] = null;
}
append(data){
let node = new Node(data);
let head = this[HEAD];
if( head === null ){
this[HEAD]=node;
}else{
while(head.next!==null){
head = head.next;
}
head.next = node;
}
}
find({data,index}){
let arr = [];
let head = this[HEAD];
if(head===null)return arr;
if( index === undefined ){
while(head!==null){
if( head.data === data ){
arr.push(head);
}
head = head.next;
}
}
if( typeof index === "number" ){
let i = 0;
while (head!==null){
if( i === index ){
arr.push(head);
}
head = head.next;
i ++;
}
}
return arr;
}
insert({data,newData,index}){
let head = this.find({data,index})[0];
if(!head)return false;
let node = new Node(newData);
let prevNext = head.next;
head.next = node;
node.next = prevNext;
return true;
}
remove({data,index}){
let head = this[HEAD];
if( index === undefined ){
if( head.data === data ){
this[HEAD] = head.next;
return;
}
while (head.next!==null){
if( head.next.data === data ){
head.next = head.next.next;
return;
}
head = head.next;
}
}
else if( typeof index === "number" ){
if( index === 0 ){
this[HEAD] = head.next;
return;
}
let i = 1;
while(head.next!==null){
if( i === index ){
head.next = head.next.next;
return;
}
head = head.next;
i++;
}
}
}
print(){
let head = this[HEAD];
while (head !== null){
console.log(head.data);
head = head.next;
}
}
size(){
let i = 0;
let head = this[HEAD];
while (head !== null){
i ++;
head = head.next;
}
return i;
}
}
})();
2. 双向链表与循环链表
双向链表指每个节点不仅仅有next指针,还有prev执行指向它的前一个节点。
循环链表指最后一个节点的next指针不是指向null,而是指向第一个节点。
代码思路与链表类似,可自己尝试实现。
3. 总结
与数组对比:①.取节点更麻烦,②.获取节点后做对应的添加和移除很方便,……所以当我们需要对数据进行多次的新增和移除操作时,选用链表结构。
五、集合
1. 创建集合结构
集合由一组无序且唯一的数据组成。是的没错,ES6的Set结构就是集合,无需我们自己再实现。接下来我们基于Set数据结构进行讨论。
回顾Set的apiadd delete has clear size ,以及初始传参。
2. 并集.交集.差集.子集
- 并集 — 传入两个集合,返回两个集合的合集
function union(a,b){
return new Set([...a,...b]);
}
- 交集 — 传入两个集合,返回两个集合共有的数据集合
function intersection(a,b){
let set = new Set();
for (let item of a) {
if( b.has(item) ){
set.add(item);
}
}
return set;
}
- 差集 — 传入两个集合,返回a集合中不存在于b集合的数据集合
function difference(a,b){
let set = new Set();
for (let item of a) {
if( !b.has(item) ){
set.add(item);
}
}
return set;
}
- 子集 — 传入两个集合,检测a集合是不是b集合的子集
function subset(a,b){
for (let item of a) {
if( !b.has(item) ){
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
六、字典
1. 创建字典结构
字典是一种以[键,值]的形式存储数据的数据结构,键用来查找查找对应的值。就像字典里面每个字(键)对应的有它的解释(值),再比如电话薄,名字(键)对应电话(值)。
Es6中的Map数据结构就是一种字典。
自己实现字典:
设置数据(set)
获取数据(get)
删除数据(delete)
是否存在(has)
返回长度(size)
let Map = (function(){
let symbol = Symbol();
return class{
constructor(){
this[symbol] = [];
}
set(key,value){
//遍历以检测是否有存在
for (let i = 0,len=this.size(); i < len; i++) {
let item = this[symbol][i];
if( item[0] === key ){
item[1] = value;
return;
}
}
this[symbol].push([key,value]);
}
get(key){
for (let i = 0,len=this.size(); i < len; i++) {
let item = this[symbol][i];
if( item[0] === key ){
return item[1];
}
}
return undefined;
}
delete(key){
for (let i = 0,len=this.size(); i < len; i++) {
let item = this[symbol][i];
if( item[0] === key ){
this[symbol].splice(i,1);
break;
}
}
}
has(key){
for (let i = 0,len=this.size(); i < len; i++) {
let item = this[symbol][i];
if( item[0] === key ){
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
size(){
return this[symbol].length;
}
}
})();
let map = new Map();
map.set("afei" , "15575127515");
map.set("zhuque" , "777");
map.set("xinai" , "55555");
map.set("afei" , "155");
console.log(map);
console.log(map.get("zhuque"));
console.log(map.has("xinai"));
console.log(map.has("ZHAOGE"));
map.delete("afei");
console.log(map.size());
七、哈希表
1. 创建哈希表结构
哈希表也叫散列表也是一种基于键值对存储值的一种数据结构,与之前的区别在于,哈希表能快速的定位值的位置,而不需要逐个遍历匹配。
JavaScript中的对象就具有哈希表结构的特性。
先忘记掉js的对象,我们通过数组来模拟一个哈希表。通过一系列的计算通过key值得到对应的序号,这个计算过程是建立哈希表最重要的过程,叫做哈希函数。比如我们可以通过每个字符的ANSII码相加得到对应的哈希索引:
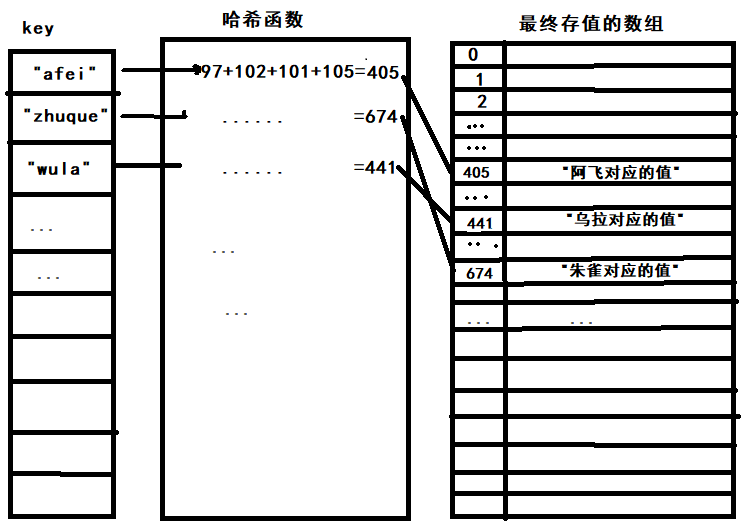
let HashTable = (function(){
let symbol = Symbol();
let hashCode = function(key){
let hash = 0;
for(let i=0;&ilt;key.length;i++){
hash += key.charCodeAt(i);
}
return hash;
};
return class{
constructor(){
this[symbol] = [];
}
set(key,value){
this[symbol][hashCode(key)] = value;
}
get(key){
return this[symbol][hashCode(key)];
}
}
})();
let h1 = new HashTable;
h1.set("afei","15575127515")
h1.set("zhuque","15714565897")
h1.set("xinai","15666666666")
console.log(h1);
很显然,这个哈希函数是很不合理的,第一,哈希值太大,只需要存三个数据却建立了一个长度好几百的数组,一般合理的利用率范围是 0.6-0.9,也就是说数据个数与总长度的比例在这之间。第二,容易出现重复,要是某两个字符码加起来刚好一样就会出现哈希值重复,从而覆盖前一个数据。
//解决第一个问题,我们可以预先设置一个较为合理的数组长度,然后规定序号不会超过长度:
//解决第二个问题,可以结合我们讲过的链表结构来存储,或者线性探查逐位往后推的方法:
//设定长度37,使用链表来解决冲突(使用质数来定长度是最合适的选择)
let LinkedList = (function(){
let HEAD = Symbol();
class Node{
constructor(data){
this.data = data;
this.next = null;
}
}
return class{
constructor(){
this[HEAD] = null;
}
append(data){
let node = new Node(data);
let head = this[HEAD];
if( head === null ){
this[HEAD]=node;
}else{
while(head.next!==null){
head = head.next;
}
head.next = node;
}
}
find({data,index}){
let arr = [];
let head = this[HEAD];
if(head===null)return arr;
if( index === undefined ){
while(head!==null){
if( head.data === data ){
arr.push(head);
}
head = head.next;
}
}
if( typeof index === "number" ){
let i = 0;
while (head!==null){
if( i === index ){
arr.push(head);
}
head = head.next;
i ++;
}
}
return arr;
}
insert({data,newData,index}){
let head = this.find({data,index})[0];
if(!head)return false;
let node = new Node(newData);
let prevNext = head.next;
head.next = node;
node.next = prevNext;
return true;
}
remove({data,index}){
let head = this[HEAD];
if( index === undefined ){
if( head.data === data ){
this[HEAD] = head.next;
return;
}
while (head.next!==null){
if( head.next.data === data ){
head.next = head.next.next;
return;
}
head = head.next;
}
}
else if( typeof index === "number" ){
if( index === 0 ){
this[HEAD] = head.next;
return;
}
let i = 1;
while(head.next!==null){
if( i === index ){
head.next = head.next.next;
return;
}
head = head.next;
i++;
}
}
}
print(){
let head = this[HEAD];
while (head !== null){
console.log(head.data);
head = head.next;
}
}
size(){
let i = 0;
let head = this[HEAD];
while (head !== null){
i ++;
head = head.next;
}
return i;
}
getHead(){
return this[HEAD];
}
}
})();
let HashTable = (function(){
let symbol = Symbol();
let hashCode = function(key){
let hash = 0;
for(let i=0;&ilt;key.length;i++){
hash += key.charCodeAt(i);
}
return hash
};
let ValuePair = class{
constructor(key,value){
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
}
}
return class{
constructor(){
this[symbol] = [];
}
set(key,value){
let index = hashCode(key);
if( !this[symbol][index] ){
this[symbol][index] = new LinkedList();
}
this[symbol][index].append(new ValuePair(key,value));
}
get(key){
let index = hashCode(key);
let linked = this[symbol][index];
if( !linked )return undefined;
let head = linked.getHead();
while (head){
if( head.data.key === key ){
return head.data.value;
}
head = head.next;
}
return undefined;
}
}
})();
let h1 = new HashTable;
h1.set("afei","15575127515")
h1.set("zhuque","15714565897")
h1.set("xinai","15666666666")
h1.set("feia","15666666666")
console.log(h1);
console.log(h1.get("afei"));
console.log(h1.get("feia"));
//向下线性探索,解决冲突问题
let HashTable = (function(){
let symbol = Symbol();
let hashCode = function(key){
let hash = 0;
for(let i=0;&ilt;key.length;i++){
hash += key.charCodeAt(i);
}
return hash
};
let ValuePair = class{
constructor(key,value){
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
}
}
return class{
constructor(){
this[symbol] = [];
}
set(key,value){
let index = hashCode(key);
while(this[symbol][index]){
if( this[symbol][index].key === key )break;
index ++;
index
}
this[symbol][index] = new ValuePair(key,value);
}
get(key){
let index = hashCode(key);
let baseIndex = index;
if(!this[symbol][index])return undefined;
while (this[symbol][index]){
if( this[symbol][index].key === key ){
return this[symbol][index].value;
}
index ++;
index
if( baseIndex === index )return undefined;
}
}
}
})();
let h1 = new HashTable;
h1.set("afei","15575127515")
h1.set("zhuque","15714565897")
h1.set("xinai","15666666666")
h1.set("feia","15666666666")
console.log(h1);
console.log(h1.get("afei"));
console.log(h1.get("feia"));
2. 有名的哈希函数
刚刚我们写的hash函数并不优秀,因为出现重复的概率比较高。下面列出一些程序猿前辈们总结的好用的hash函数,大家可以先感受一下
//DJB
function DJBHash(str) {
var hash = 5381;
var len = str.length , i = 0
while (len--){
hash = (hash << 5) + hash + str.charCodeAt(i++); /* times 33 */
}
hash &= ~(1 << 31); /* strip the highest bit */
return hash;
}
//JS
function JSHash(str) {
var hash = 1315423911;
for(var i = 0; i < str.length; i++) {
hash ^= ((hash << 5) + str.charCodeAt(i) + (hash >> 2));
}
return hash;
}
//PJW
function PJWHash( str) {
var BitsInUnsignedInt = 4 * 8;
var ThreeQuarters = (BitsInUnsignedInt * 3) / 4;
var OneEighth = (BitsInUnsignedInt / 8);
var HighBits = (0xFFFFFFFF) << (BitsInUnsignedInt - OneEighth);
var hash = 0;
var test = 0;
for(var i = 0; i < str.length; i++) {
hash = (hash << OneEighth) + str.charCodeAt(i);
if((test = hash & HighBits) != 0)
{
hash = (( hash ^ (test >> ThreeQuarters)) & (~HighBits));
}
}
return hash;
}
……
八、树
1. 了解树结构
树是一种重要的非线性结构,以分层的方式存储数据,比如公司的组织架构。
顶部节点叫做根节点,其他节点都是它的子节点,有子元素的节点称为内部节点,没有子元素的节点称为外部节点或叶节点。每个节点有层次,比如图中B节点层次为1,A节点层次为0,树种最大的层次称为该树的深度。每个节点和它的子节点组成子树。
2. 二叉树与二叉搜索树
二叉树在计算机科学中应用非常广泛。它是一种特殊的树,每个节点最多拥有左右两个子节点。利用它的特性我们可以更高效的对树中数据进行 增 删 查等操作。
二叉搜索树(BinarySearchTree)是二叉树的一种,它只允许在节点的左侧存储比节点小的值,在节点右侧存储比节点大(或等于)的值。
实现二叉搜索树:
插入节点 insert
let BST = (function(){
class Node{
constructor(data){
this.data = data;
this.left = null;
this.right = null;
}
}
let root = Symbol();
function insertNode(node,root) {
if (node.data < root.data) {
if (root.left) {
insertNode(node,root.left);
} else {
root.left = node;
}
}else{
if( root.right ){
insertNode(node,root.right);
}else{
root.right = node;
}
}
}
return class{
constructor(){
this[root] = null;
}
insert(data){
let node = new Node(data);
if (this[root] !== null) {
insertNode(node,this[root]);
} else {
this[root] = node;
}
}
}
})();
let bst = new BST();
bst.insert(9);
bst.insert(5);
bst.insert(4);
bst.insert(51);
bst.insert(88);
bst.insert(76);
bst.insert(23);
bst.insert(7);
bst.insert(1);
console.log(bst);
3. 树的遍历
讲课的时候分开讲每一种遍历的代码,课件里面代码我全放后面……
- 中序遍历针对每棵树都是左根右的顺序遍历数据:
- 先续遍历针对每棵树都是根左右的顺序遍历:团懒得画了
- 后续遍历针对每棵树都是左右根的顺序遍历:懒得画+1
let BST = (function(){
class Node{
constructor(data){
this.data = data;
this.left = null;
this.right = null;
}
}
let root = Symbol();
function insertNode(node,root) {
if (node.data < root.data) {
if (root.left) {
insertNode(node,root.left);
} else {
root.left = node;
}
}else{
if( root.right ){
insertNode(node,root.right);
}else{
root.right = node;
}
}
}
function inOrderTraverseNode(node,arr){
if( node === null )return;
inOrderTraverseNode(node.left,arr);
arr.push(node.data);
inOrderTraverseNode(node.right,arr);
}
function preOrderTraverseNode(node,arr){
if( node === null )return;
arr.push(node.data);
preOrderTraverseNode(node.left,arr);
preOrderTraverseNode(node.right,arr);
}
function postOrderTraverseNode(node,arr){
if( node === null )return;
postOrderTraverseNode(node.left,arr);
postOrderTraverseNode(node.right,arr);
arr.push(node.data);
}
return class{
constructor(){
this[root] = null;
}
insert(data){
let node = new Node(data);
if (this[root] !== null) {
insertNode(node,this[root]);
} else {
this[root] = node;
}
}
inOrderTraverse(){
let arr = [];
inOrderTraverseNode(this[root],arr);
return arr;
}
preOrderTraverse(){
let arr = [];
preOrderTraverseNode(this[root],arr);
return arr;
}
postOrderTraverse(){
let arr = [];
postOrderTraverseNode(this[root],arr);
return arr;
}
}
})();
let bst = new BST();
bst.insert(9);
bst.insert(5);
bst.insert(4);
bst.insert(51);
bst.insert(88);
bst.insert(76);
bst.insert(23);
bst.insert(7);
bst.insert(1);
console.log(bst);
console.log(bst.inOrderTraverse()); //在二叉搜索树种,这种方式正好可以得到顺序排列的数组
console.log(bst.preOrderTraverse());
console.log(bst.postOrderTraverse());
4. 查找与删除
//获取最小值 getMin
//获取最大值 getMax
//检测值是否存在 has
//移除值 remove
let BST = (function(){
let ROOT = Symbol();
class Node{
constructor(data){
this.data = data;
this.left = null;
this.right = null;
}
}
function insertNode(node,root) {
if (node.data < root.data) {
if (root.left) {
insertNode(node,root.left);
} else {
root.left = node;
}
}else{
if( root.right ){
insertNode(node,root.right);
}else{
root.right = node;
}
}
}
function inOrderTraverseNode(node,arr){
if( node === null )return;
inOrderTraverseNode(node.left,arr);
arr.push(node.data);
inOrderTraverseNode(node.right,arr);
}
function preOrderTraverseNode(node,arr){
if( node === null )return;
arr.push(node.data);
preOrderTraverseNode(node.left,arr);
preOrderTraverseNode(node.right,arr);
}
function postOrderTraverseNode(node,arr){
if( node === null )return;
postOrderTraverseNode(node.left,arr);
postOrderTraverseNode(node.right,arr);
arr.push(node.data);
}
function hasData(node,data) {
if( !node )return false;
if( datanode.data ){
return hasData(node.right,data);
}else{
return false;
}
}
function getMin(node){
while(node.left){
node = node.left;
}
return node;
}
function removeNode(node,data) {
if( !node )return node;
if( node.data < data ){
node.right = removeNode(node.right,data);
}else if( node.data > data ){
node.left = removeNode(node.left,data);
}else{
if( node.left === null && node.right === null ){
node = null;
return node;
}
if( node.left === null){
node = node.right;
return node;
}
if( node.right === null ){
node = node.left;
return node;
}
if( node.left && node.right ){
//方案1:左树最大值 或者 右树最小值 充当删除的这个值的位置
//方案2:把左树放置到右树的最左端
//方案3:把右树放置到左树的最右端
//方案1 ——
let min = getMin(node.right);
node.data = min.data;
node.right = removeNode(node.right,min.data);
return node;
}
}
}
return class{
constructor(){
this[ROOT] = null;
}
insert(data){
let node = new Node(data);
if (this[ROOT] !== null) {
insertNode(node,this[ROOT]);
} else {
this[ROOT] = node;
}
}
inOrderTraverse(){
let arr = [];
inOrderTraverseNode(this[ROOT],arr);
return arr;
}
preOrderTraverse(){
let arr = [];
preOrderTraverseNode(this[ROOT],arr);
return arr;
}
postOrderTraverse(){
let arr = [];
postOrderTraverseNode(this[ROOT],arr);
return arr;
}
getMin(){
let root = this[ROOT];
if(!root)return null;
while (root.left)root = root.left;
return root.data;
}
getMax(){
let root = this[ROOT];
if(!root)return null;
while (root.right)root = root.right;
return root.data;
}
has(data){
return hasData(this[ROOT],data);
}
remove(data){
this[ROOT] = removeNode(this[ROOT],data);
}
}
})();
5. 平衡二叉树
二叉搜索树有可能出现的一种情况是某一条分支深度特别大,而其他的分支深度很低。为了解决这个问题,有一种树叫做平衡二叉树(作者是 Adelson Velskii 和 Landi,所以也叫AVL树)。自平衡树在添加节点时,会按情况分配,保证树中任意节点的左子树和右子树的深度差不超过1。
创建平衡二叉树:
let AVL = (function(){
let ROOT = Symbol();
class Node{
constructor(key){
this.key = key;
this.left = null;
this.right = null;
}
}
//插入节点
function insertNode(root,node) {
if( !root )return node;
if( node.key < root.key ){
root.left = insertNode(root.left,node);
//检测树深度失衡
if( NodeDeep(root.left) - NodeDeep(root.right) > 1 ){
if( node.key < root.left.key ){
//左左
root = LL(root);
}else{
//左右
root = LR(root);
}
}
}else{
root.right = insertNode(root.right,node);
//检测树深度失衡
if( NodeDeep(root.right) - NodeDeep(root.left) > 1 ){
if( node.key < root.right.key ){
//右左
root = RL(root);
}else{
//右右
root = RR(root);
}
}
}
return root;
}
//计算树深度
function NodeDeep(node) {
if(!node)return 0;
return Math.max(NodeDeep(node.right),NodeDeep(node.left)) + 1;
}
//第一种情况,左左 LL
function LL(node) {
let tmp = node.left;
node.left = tmp.right;
tmp.right = node;
return tmp;
}
//第二种情况,右右 RR
function RR(node) {
let tmp = node.right;
node.right = tmp.left;
tmp.left = node;
return tmp;
}
//第三种情况,左右 LR
function LR(node) {
node.left = RR(node.left);
return LL(node);
}
//第四种情况,右左 RL
function RL(node) {
node.right = LL(node.right);
return RR(node);
}
return class {
constructor(){}
insert(key){
this[ROOT] = insertNode(this[ROOT],new Node(key));
}
}
})();
let avl = new AVL;
avl.insert(50)
avl.insert(30)
avl.insert(60)
avl.insert(58)
avl.insert(80)
avl.insert(59)
avl.insert(90)
avl.insert(100)
console.log(avl);
6. 红黑树
红黑树(Red Black Tree) 是平衡二叉树的一种。红黑树是一种特化的AVL树,在进行插入和删除操作时通过特定操作保持二叉查找树的平衡,从而获得较高的查找性能。它虽然是复杂的,但它的最坏情况运行时间也是非常良好的,并且在实践中是高效的。 它可以在O(log n)时间内做查找,插入和删除,这里的 n 是树中元素的数目。
红黑树的特点:
- 节点必须是红色或黑色
- 根节点是黑色
- 所有叶子是都黑色(叶子是指null节点)
- 每个红色节点的子节点都是黑色(不能有连续的红节点)
- 任一节点到其每个叶子的所有路径都包含相同数量的黑色节点
红黑树例图:

创建红黑树:
// 红黑树模型
// 红黑树节点颜色常量
const RED = 'RED';
const BLACK = 'BLACK';
class Node {
constructor(key) {
this.key = key;
this.left = null;
this.right = null;
this.parent = null;
this.color = RED; // 新节点默认是红色
}
}
// 红黑树模型
class RedBlackTree {
constructor() {
this.root = null;
}
// 插入节点
insert(key) {
let newNode = new Node(key);
let current = this.root;
let parent = null;
if (this.root === null) {
this.root = newNode;
newNode.color = BLACK;
return;
}
// 查找插入位置
while (current !== null) {
parent = current;
if (key < current.key) {
current = current.left;
} else {
current = current.right;
}
}
newNode.parent = parent;
if (key < parent.key) {
parent.left = newNode;
} else {
parent.right = newNode;
}
// 修复红黑树性质
this.fixInsert(newNode);
}
// 插入后修复红黑树结构
fixInsert(node) {
while (node !== this.root && node.parent.color === RED) {
let parent = node.parent;
let grandparent = parent.parent;
if (parent === grandparent.left) {
let uncle = grandparent.right;
if (uncle && uncle.color === RED) {
// 情况1:叔叔是红色
parent.color = BLACK;
uncle.color = BLACK;
grandparent.color = RED;
node = grandparent;
} else {
if (node === parent.right) {
// 情况2:叔叔是黑色,且当前节点是右子
node = parent;
this.leftRotate(node);
}
// 情况3:叔叔是黑色,当前节点是左子
parent.color = BLACK;
grandparent.color = RED;
this.rightRotate(grandparent);
}
} else {
// 对称情况:父节点是右子节点
let uncle = grandparent.left;
if (uncle && uncle.color === RED) {
parent.color = BLACK;
uncle.color = BLACK;
grandparent.color = RED;
node = grandparent;
} else {
if (node === parent.left) {
node = parent;
this.rightRotate(node);
}
parent.color = BLACK;
grandparent.color = RED;
this.leftRotate(grandparent);
}
}
}
this.root.color = BLACK;
}
leftRotate(x) {
let y = x.right;
x.right = y.left;
if (y.left !== null) {
y.left.parent = x;
}
y.parent = x.parent;
if (x.parent === null) {
this.root = y;
} else if (x === x.parent.left) {
x.parent.left = y;
} else {
x.parent.right = y;
}
y.left = x;
x.parent = y;
}
rightRotate(y) {
let x = y.left;
y.left = x.right;
if (x.right !== null) {
x.right.parent = y;
}
x.parent = y.parent;
if (y.parent === null) {
this.root = x;
} else if (y === y.parent.left) {
y.parent.left = x;
} else {
y.parent.right = x;
}
x.right = y;
y.parent = x;
}
}
九、图
1. 了解图结构
图由节点(顶点)和边组成,节点之间由边连接,一个边连接两个节点,一个节点可以对应很多条边(这些边的数量称为这个节点的度)。相邻节点按顺序组成的序列叫路径。路径中没有重复节点的叫做简单路径。路径中最后一个顶点和第一个顶点相同的构成环。有向图的边是带箭头的(有序的)。每个节点之间都有边的图叫强连通图。
2. 创建图
要存储图中的节点,并且表明节点间边的关系,我们可以采用多种方式来实现。常见的有邻接矩阵和邻接表。邻接矩阵使用二维数组来描述节点间连接关系,但是当节点比边多很多时,会有很多空位浪费。邻接表采用字典(也可以是表,数组)来存储节点和它对应连接的节点关系,具体模型图请看课程讲解。
使用邻接表的方案来实现图:
//图结构 类
let Graph = class {
constructor(){
//存储所有顶点
this.vertices = [];
//存储每个顶点对应的相邻顶点(边)
this.edges = {};
}
//添加顶点
addVertex(...rest){
rest.forEach(v=>{
//如果顶点已经添加,return
if( this.vertices.includes(v) )return;
//顶点不存在
//添加顶点
this.vertices.push(v);
//初始化顶点的边存储信息
this.edges[v] = [];
});
}
//添加边
addEdge(v1,v2){
//添加节点
this.addVertex(v1,v2);
//如果双方已经添加过对应的信息,返回
if( this.edges[v1].includes(v2) )return;
//双方互相添加边信息
this.edges[v1].push(v2);
this.edges[v2].push(v1);
}
};
let graph = new Graph;
graph.addEdge("A" , "B");
graph.addEdge("A" , "C");
graph.addEdge("A" , "E");
graph.addEdge("B" , "D");
graph.addEdge("B" , "E");
graph.addEdge("C" , "F");
graph.addEdge("E" , "F");
console.log(graph);
3. 遍历
图的遍历有两种算法:广度优先(Breadth-First Search)\和深度优先(Depth-First Search)。遍历图可以查找某个顶点、寻找两个顶点间的路径、检测图是否连通、检测图是否有环等。
遍历思路:将各个顶点分为三种状态-白、灰、黑,白色代表未被发现,灰色代表已被发现但未被探索,黑色代表已被发现并被探索。广度优先遍历过程是,先发现节点所有相邻节点,再遍历这些节点继续按规则往下遍历。深度优先遍历过程是,找到一个相邻节点后,立即再继续找它的相邻节点,以此类推。
//图结构 类
let Graph = (function(){
//队列类,辅助广度优先遍历
class Queue{
constructor(){
this.items = [];
}
enqueue(data){
this.items.push(data);
}
dequeue(){
return this.items.shift();
}
size(){
return this.items.length;
}
}
//图类
return class {
constructor(){
//存储所有顶点
this.vertices = [];
//存储每个顶点对应的相邻顶点(边)
this.edges = {};
}
//添加顶点
addVertex(...rest){
rest.forEach(v=>{
//如果顶点已经添加,return
if( this.vertices.includes(v) )return;
//顶点不存在
//添加顶点
this.vertices.push(v);
//初始化顶点的边存储信息
this.edges[v] = [];
});
}
//添加边
addEdge(v1,v2){
//添加节点
this.addVertex(v1,v2);
//如果双方已经添加过对应的信息,返回
if( this.edges[v1].includes(v2) )return;
//双方互相添加边信息
this.edges[v1].push(v2);
this.edges[v2].push(v1);
}
//广度优先
bfs(v){
let vertices = this.vertices,
edges = this.edges,
color = {},
queue = new Queue()
;
//对每个顶点添加状态标志
vertices.forEach(v=>{
color[v] = "white";
});
//入口顶点入队及状态改变
queue.enqueue(v);
color[v] = "grey";
//循环出队进行发现或探索
while (queue.size()){
//取出队首顶点
let u = queue.dequeue();
//获取顶点对应的相邻顶点
let edg = edges[u];
//测试打印
let s = u+"===>"
//探索
edg.forEach(v=>{
if(color[v] !== "white")return;
s += v+" "
queue.enqueue(v);
color[v] = "grey";
});
//探索完,改变状态
color[u] = "black";
console.log(s);
}
}
};
})();
let graph = new Graph;
graph.addEdge("A" , "B");
graph.addEdge("A" , "C");
graph.addEdge("A" , "E");
graph.addEdge("B" , "D");
graph.addEdge("B" , "E");
graph.addEdge("C" , "F");
graph.addEdge("E" , "F");
graph.bfs("A");
//图结构 类
let Graph = (function(){
//队列类,辅助广度优先遍历
class Queue{
constructor(){
this.items = [];
}
enqueue(data){
this.items.push(data);
}
dequeue(){
return this.items.shift();
}
size(){
return this.items.length;
}
}
//图类
return class {
constructor(){
//存储所有顶点
this.vertices = [];
//存储每个顶点对应的相邻顶点(边)
this.edges = {};
}
//添加顶点
addVertex(...rest){
rest.forEach(v=>{
//如果顶点已经添加,return
if( this.vertices.includes(v) )return;
//顶点不存在
//添加顶点
this.vertices.push(v);
//初始化顶点的边存储信息
this.edges[v] = [];
});
}
//添加边
addEdge(v1,v2){
//添加节点
this.addVertex(v1,v2);
//如果双方已经添加过对应的信息,返回
if( this.edges[v1].includes(v2) )return;
//双方互相添加边信息
this.edges[v1].push(v2);
this.edges[v2].push(v1);
}
//最短路径
BFS(v){
let vertices = this.vertices,
edges = this.edges,
color = [],
queue = new Queue(),
info = {}
;
//状态初始化
vertices.forEach(v=>{
color[v] = "white";
});
//入口顶点入队 状态改变 初始信息
queue.enqueue(v);
color[v] = "grey";
info[v] = {distance : 0, path : v};
//发现与探索
while (queue.size()){
let u = queue.dequeue();
edges[u].forEach(v=>{
if(color[v]!=="white")return;
color[v] = "grey";
queue.enqueue(v);
info[v] = {
distance : info[u].distance + 1,
path : info[u].path + "->" + v
};
});
color[u] = "black";
}
/*
返回信息的期望状态
{
"A" : {distance:0,path:"A"}
"B" : {distance:1,path:"A-B"}
"C" : {distance:1,path:"A-C"}
"D" : {distance:2,path:"A-B-D"}
"E" : {distance:1,path:"A-E"}
"F" : {distance:2,path:"A-C-F"}
}
*/
return info;
}
};
})();
let graph = new Graph;
graph.addEdge("A" , "B");
graph.addEdge("A" , "C");
graph.addEdge("A" , "E");
graph.addEdge("B" , "D");
graph.addEdge("B" , "E");
graph.addEdge("C" , "F");
graph.addEdge("E" , "F");
console.log(graph.BFS("D")); 

评论(0)
暂无评论